Each one of us must have heard the terms blockchain and cryptocurrency and Bitcoin. But how many of us know what these terms mean and understand the differences? Most of us believe the terms sound very complicated and do not want to venture into them.
But the reality is the basic concept of blockchain is quite simple for anyone to understand and start exploring this technology. Blockchain technology was introduced to the world through the cryptocurrency Bitcoin. Since then, blockchain has gained popularity in the financial sector. It is still growing with the discovery of its application in various other industries.
As per Statista, there has been worldwide spending of 6.6 bn USD in the year 2021 on blockchain solutions. The banking sector has the highest distribution of Blockchain market value in the world with cross-border payments and settlements.
The entire world is slowly turning its head towards blockchain technology. In the Gartner 2019 CIO Agenda Survey, over 60% of CIOs across various sectors expected some level of blockchain technology adoption into their infrastructure in the next three years.
It has thus become hard to be ignorant about an upcoming and booming technology like blockchain. It is time for us to jump onto the bandwagon and upgrade ourselves with this new technology so that we can remain at the forefront of this technology.
What is Blockchain?
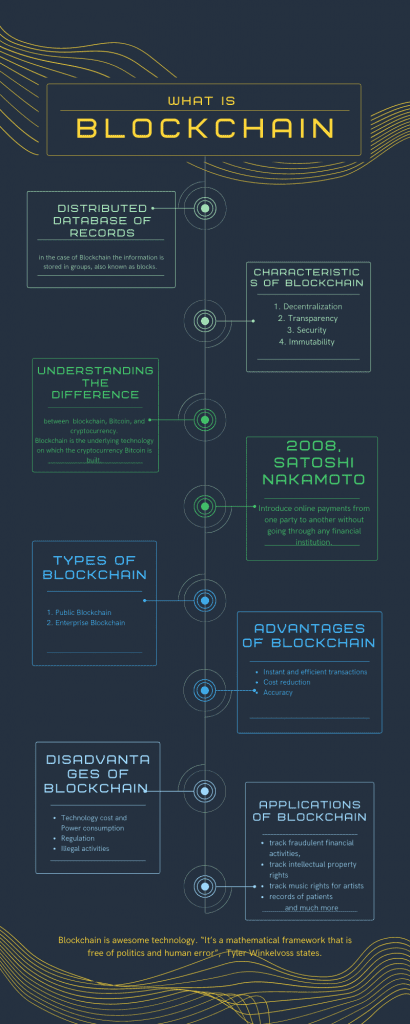
Blockchain is a distributed database of records or public ledger of transactions across a peer-to-peer network. It is primarily a type of database. We know that a database is a collection of information structured in a table format. These structures of information are stored electronically in a computer system. While in the case of Blockchain the information is stored in groups, also known as blocks.
Each of these blocks contains sets of information or transactions with a storage limit to it. Once this limit for a block is reached, it is linked to the previous block, thus forming a chain of all the blocks of information. Every new set of information is added to a newly formed block. Once this block gets filled up to its capacity, it is added to this chain of blocks.
Since all these blocks of data and transactions are linked to each other in the form of a chain, no changes can be made to any data in any block. Any change in any block will result in subsequent changes in every other block, thus making it clear that the blockchain has been tampered with. This makes it almost impossible to hack or corrupt the blockchain system as it will lead to making changes to every other block.
Characteristics of Blockchain
1. Decentralization
One of the most important characteristics of blockchain technology is decentralization. No single computer system or organization can own an entire blockchain. A blockchain consists of a collection of computer systems across different geographic locations and is operated by different individuals or groups of individuals.
These computers that make up the blockchain are called nodes. Every node has a copy of the blockchain and thus contains all the data since the inception of the blockchain. Making changes in one node will require making changes to every other node in the blockchain. This makes it impossible to make changes or tamper with data at any node since all the other nodes can cross-reference and point out where the issue is.
2. Transparency
Every individual or group of individuals that have access to a node in the blockchain will have a copy of the blockchain and thus all the information stored in it. In the case of Bitcoin’s blockchain, an individual can use blockchain explorers to access all the information for the blockchain.
Every node gets updated as soon as new blocks are created and added to the blockchain. This allows every individual or group of individuals to have complete knowledge of all the data and transaction information stored in a blockchain. This ensures transparency for every user of blockchain.
3. Security
As we know in a blockchain, every new block is added to the end of the blockchain linearly and chronologically. Every block in the blockchain has its unique hash and the reference of the previous block’s hash in the blockchain. It also contains the previously mentioned timestamp.
A math function is used to create the hash that turns digital information into a string of letters and numbers. If any changes are made to this information, it changes the hash code as well. Changes made to a single copy or a few of them will lead to non-alignment with the other copies of the blockchain. This will help to cross-reference and find the faulty copy and discard it.
This will help the blockchain from being hacked and thus ensure the security of all the information and transactions stored on the blockchain.
4. Immutability
The information or transactions entered into the blockchain cannot be altered. To update any information or transaction in the blockchain, another record of the information or transaction can be entered. This way, the original transaction cannot be deleted or hidden. We can always find out where it is, where it’s been, and its entire lifecycle.
Blockchain, like Bitcoin, has its ledgers in a forwarding momentum that are never-ending. For anyone to control the Bitcoin market will need control over 51% of the total market. Ledgers can be changed by hard fork where an unchangeable permanent modification can be made to the blockchain.
This can be done when there is an agreement amongst the miners, node operators, exchange, and individual users. This is an exhaustive process, and the chances are more that the old ledgers will remain in their original form. This primarily shows how information and transactions on the blockchain are irreversible.
Understanding the difference between Blockchain, Bitcoin, and Cryptocurrency
We have heard the terms blockchain, Bitcoin, and cryptocurrency on various occasions, and we tend to use these terms interchangeably. Blockchain is the underlying technology on which the cryptocurrency Bitcoin is built. Bitcoin is one of the numerous cryptocurrencies in the market, but all of them use blockchain technology.
In the year 2008, an individual or a group of individuals under the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto published a paper named “Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System”. The main aim here was to make online payments from one party to another without going through any financial institution.
In this case, Bitcoin merely uses blockchain as a means to record a ledger of payments transparently. But blockchain can be used to immutably record any kind and number of data points right from different transactions to votes in an election to product inventories and much more.
We can conclude by saying Blockchain is the technology behind Bitcoin and many other cryptocurrencies like Ethereum, Litecoin, etc. Blockchain is currently being explored in many fields of application other than cryptocurrency.
Types of Blockchain
Blockchain technology was introduced with Bitcoin, but now this technology has gained popularity and various organizations are exploring this technology across different sectors. Blockchain technology can now be broadly classified into Public Blockchain and Enterprise Blockchain.
1. Public Blockchain
Public blockchains are an open and decentralized network of computers that are accessible to anyone with an internet connection. There are no restrictions and anyone can start validating blocks in a blockchain and send transactions. These networks offer incentives to these users or miners that validate blocks.
A public blockchain functions through a Proof of Work and Proof of Stake consensus algorithm. These consensus algorithms are used for validating transactions without a third party, like a bank.
The public blockchain is completely decentralized and no single organization has control over the ecosystem. It does not require a third party, thus making it self-governed and an autonomous digital public ledger.
Almost all the big players in the crypto world use public blockchain like Bitcoin, Ethereum, and many more. Its true advantages are greater transparency, decentralized structure, user empowerment, and immutability which makes it the ideal mode and lucrative to the industry.
2. Enterprise Blockchain
An enterprise blockchain is a permissioned blockchain that can be integrated and utilized to streamline business processes at scale. Many corporations believe that this type of blockchain is preferable to public blockchain since data visibility and access can be restricted to a select group of people.
Enterprise blockchain is permissioned, and that allows companies to have direct control over them. The main advantages of enterprise blockchain are accountability, permissioned, mutability, and scalability.
Enterprise blockchain can be categorized as Private and Consortium.
- A Private blockchain is mainly used within an organization where access is restricted to only a closed network of members. It is suitable for companies that want to use blockchain only for internal use. Here the organization has complete control over the network and can make and change the rules as per their requirements.
- A Consortium blockchain is ideal for organizational collaboration where a group of two or more parties jointly define the rules of the network. Each of the entities can contribute to the network. This allows scalability and more security to the network.
Advantages of blockchain
- Instant and efficient transactions – Blockchain technology transactions can take place in minutes which is not possible in the case of traditional banks. This helps particularly in the case of cross-border transactions.
- Cost reduction – Blockchain eliminates the involvement of third-party in any transaction thus eliminating the costs associated with them.
- Accuracy – Transactions in a blockchain are verified by thousands of computers in the network. This eliminates human intervention resulting in less human error and accurate record of information.
Disadvantages of Blockchain
- Technology cost and Power consumption – Blockchain saves money for users through transaction fees but the cost of technology shoots up because of the high-power consumption to support millions of computers. Mining costs and validating transactions in blockchain drives up the electricity bills for the users leading to more power consumption.
- Regulation – There are growing concerns about government regulation of cryptocurrencies. In the modern world, money has been created and controlled by central governments. It becomes a hurdle for cryptocurrencies to get accepted by pre-existing financial institutions.
- Illegal activities – Blockchain technology is open for access to any person. There are no checks or verifications done on the users who can access the blockchain. This allows criminals or suspects to easily transact on blockchain leading to illicit transactions being undertaken in the blockchain.
Applications of Blockchain
Blockchain applications currently go far beyond just cryptocurrency and Bitcoin. It is seen that blockchain has an endless number of applications across various industries with its ability to create transparency and fairness while saving businesses time and resources.
The ledger technology in blockchain has numerous applications across various sectors. To list a few, it can be used to track fraudulent activities in the financial sector and track intellectual property rights in business. It can be used to track music rights for artists in the entertainment industry. It can also be used to securely share records of patients with healthcare professionals.
Big organizations are already investing huge amounts to develop this technology for their organizations. It has shown a lot of promise in real-world use cases like faster cross-border payments and smart contracts. Most recently blockchain has been a key player in the fight against COVID-19 by securely storing patient information and medical research data.
Blockchain Future
Blockchain technology started with skepticism in the minds of the people and organizations. But with time blockchain technology is slowly building confidence in the people with its numerous practical applications being successfully explored and implemented.
Blockchain stands to make business operations more accurate, secure, efficient with fewer middlemen. Blockchain technology has picked up its pace and now it is no more a question of “if” for organizations to adopt blockchain rather than a question of “when”.