Blockchain is a decentralized, shared network of computers that serves as a secure payment ledger database shared by all participants.
Blockchain does this by distributing duplicates of a database over an entire network, making it impossible to attack or modify the system. Blockchain technology has a wide range of possible uses, although cryptocurrency is now its most well-known application.
Learn more about blockchain, discover how it functions, who is using it, and what the future holds for this technology.
Blockchain Explained
Blockchain is a decentralized, immutable database that streamlines the tracking of assets and the recording of transactions inside a corporate network. A resource could either be tangible (such as a house, car, cash, or piece of land) or intangible (intellectual property, patents, copyrights, branding).
One of the most significant inventions in recent memory is the Blockchain. Every industry may benefit from it, and in a variety of ways. All of the electronic data is saved in blocks in this database. It’s a database. Private keys are required to access the database, ensuring total confidentiality.
Blockchain is becoming increasingly popular across the world. Bitcoin’s rapid rise has helped spread the word about blockchain technology to investors and entrepreneurs throughout the world. Even though many people are interested in this new technology, there are still some misunderstandings.
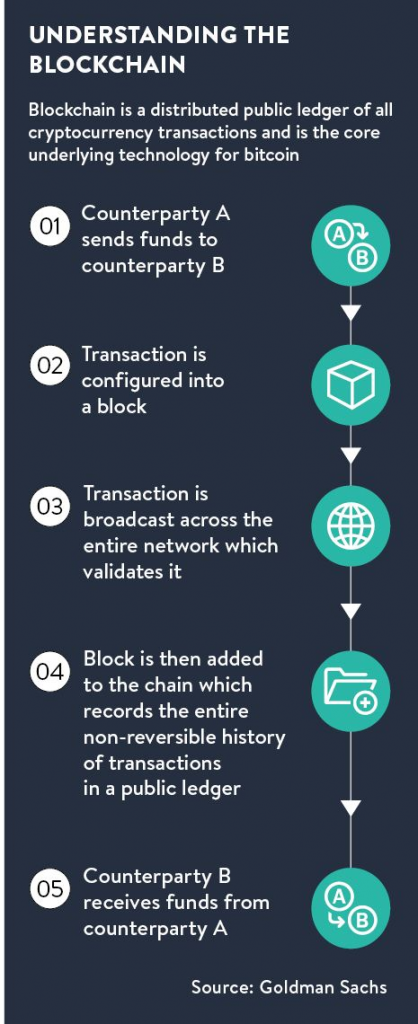
The establishment of a blockchain and the use of Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies are made feasible by cryptographic technology. This means that manipulating a single block’s data would be difficult without affecting other blocks in the chain. An authenticated product or service will lower transaction costs using this technology.
Important aspects of a blockchain:
Operations of Blockchain Technology:
- Distributed Ledger Technology: All network users can access the shared ledger’s immutable transaction record thanks to distributed ledger technology. This shared ledger eliminates the redundancy of effort found in traditional business networks by only recording transactions once.
- Immutable data: No participant is allowed to change or meddle with a transaction once it has been registered to the shared ledger. A fresh transaction must be added to undo an error in a transaction record before both transactions are displayed.
- Digital contracts: To expedite transactions, a smart contract, or set of instructions, is kept upon that blockchain and immediately executed. A smart contract can specify terms for the payment of trip insurance, corporate bond transfer requirements, and much more.
- As each transaction occurs, a “block” of data is kept on track of it. These transactions show the movement of a commodity, which could be an intangible asset or a tangible product (intellectual). The data block can be used to store information on who, what, when, where, how much, and even the circumstance as the temperature of a food shipment.
- The preceding and following blocks are linked to one another. These blocks form a chain of data as an asset is relocated to the next or ownership changes. The blocks guarantee the precision and order of operations and are linked closely together to prevent any blocks from being altered or from being added between two existing blocks.
- A blockchain is a block-joined, unbreakable sequence of transactions. Every new block strengthens the verification of the previous block and, consequently, the blockchain overall. This makes the blockchain tamper-evident and gives it its essential strength of immutability. By doing this, you and other system users may establish a reliable record of transactions and take away the opportunity for malicious actors to tamper with the data.
Comparing Public and Private Blockchains:
In a public blockchain, anyone can take part, which entitles them to read, write, or monitor the transaction information. Notably, because no single entity controls the nodes, it is exceedingly impossible to change transactions that have been recorded in a public blockchain.
A private blockchain, on the other hand, is run by a business or institution. It has the power to go back and change the blockchain, and it is the only one that can select who gets admitted to the system. Besides being distributed over numerous nodes to improve security, this private blockchain procedure is comparable to an internal data storage system.
Practical Applications of Blockchain:
From managing voting systems to offering financial services, Blockchain technology is employed for a variety of tasks which also include:
- Cryptocurrencies: Blockchain is currently most frequently used as the foundation for cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin or Ethereum. A blockchain keeps track of all cryptocurrency purchases, exchanges, and expenditures. The more cryptocurrency users there are, the more common blockchain technology may become.
- Banking: Blockchain has been used to facilitate transactions in a medium of exchange, such as dollars and euros, in addition to cryptocurrencies. Due to speedier transaction verification and processing outside of regular business hours, this may be quicker than wiring funds through a banking institution.
- Supply Chain Monitoring: Supply chains generate enormous volumes of information as objects move from one part to another. It can be challenging to identify the root cause of issues, such as the vendor from which subpar items were purchased, when using conventional data storing techniques. IBM’s Food Trust uses blockchain technology to track its food cultivation and consumption.
- Voting: Experts are investigating how to use blockchain to stop voting fraud. Theoretically, blockchain voting would make it unnecessary for individuals to physically gather and validate paper ballots by allowing voters to cast votes that couldn’t be manipulated.
Is Blockchain Safe?
Blockchain technology achieves flexible security and trust in numerous ways. Take the example of a hacker who runs a node on a blockchain network and wants to alter a blockchain to steal everyone else’s bitcoin. They could not update their copy without also changing the copies that everyone else had made.
The hacker’s version of the chain will be disregarded as fake because when everyone examines their files with one another, they will discover that this one copy sticks out. For such a hack to succeed, the hacker would have to simultaneously control and alter at least 51% of the blockchain versions, making their changed copy the dominant copy and, thus, the network that has been agreed upon.
Reasons to begin stockpiling bitcoins immediately:
We all are aware that the primary factor driving people’s willingness to spend in Bitcoin is the potential for instant millionaire status. By mining Bitcoin and purchasing it at a price below the one you intend to sell it for, you can make money. These platforms are much more than online markets because they include cutting-edge AI systems that can assist you in selling your Bitcoins for the highest price and making the biggest profit.
Many analysts think that Bitcoin will keep growing over time because of how widely accepted it is by the general public. Some of them even think the day will come when the majority of people on Earth will be using Bitcoin. Governments will be under intense public pressure at these times, and they won’t have any other option but to accept it as a valid form of payment. The most money will be made from these events by early investors.
Blockchain vs Bitcoin:
A blockchain serves as the foundation of the Bitcoin system. In a research paper that launched the virtual currency, Bitcoin’s mysterious creator Satoshi Nakamoto called it “a novel electronic cash system that is peer-to-peer, with no neutral third party.”
It’s vital to remember that only Bitcoin uses blockchain to permanently and transparently maintain a ledger of payments. However, in theory, any number of points might be permanently recorded using blockchain. Transactions, votes in politics, inventories of products, state identification cards, property deeds, and many other things could be examples of this.
Bitcoin vs Ethereum:
Although the distributed ledger and cryptography principles underlie both the Bitcoin and Ethereum networks, there are significant technical differences between the two. Data linked to operations on the Bitcoin network is frequently just for note-taking, whereas data connected to transactions on the Ethereum blockchain may include executable code.
As a replacement for conventional currencies, bitcoin is primarily intended to serve as a medium of exchange in the form of wealth. Ethereum is a flexible blockchain with use cases in Defi, smart contracts, and NFTs, among others.
Wrapping Up:
As Evan Luthra, a Blockchain expert once said “Before Google and Facebook had their first iterations, the internet had been around for nearly 15 years. Although it’s difficult to anticipate where blockchain technology will go in another ten or fifteen years, it will fundamentally alter how we transact and communicate with one another in the future, much like the internet”.
Blockchain thus offers an integrated platform for exchanging trustworthy data. We at Dappros provide a simple but vast variety of solutions to implement blockchain technology through our cloud service, on-premises edition, and supply chain SaaS application. We will be pleased if we could get an opportunity to help you in establishing a Blockchain Tech for your business.
FAQs
- What is a Blockchain in layman’s language?
A blockchain is a distributed repository or ledger. Each node in the cluster has an exact copy of the whole database, and information is stored in data models called blocks.
- How Many Live Blockchains Are There?
The number of active blockchains is rising at an exponential rate every day. By 2022, there will be several hundred additional non-crypto currency blockchains in addition to the more than 10,000 existing cryptocurrencies built on blockchain.
- Who Created Blockchain, exactly?
Stuart Haber & W. Scott Stornetta, two mathematicians interested in implementing a system where documentation timestamps could not be altered, first proposed the concept of blockchain technology in 1991.
Summary
We at Dappros constantly driving to deliver the best of our work. Check here our achievements and similar blog post for more clarity.